Crypto Staking or Crypto Mining: Making the Right Choice

Staking and mining are both methods of achieving the same ultimate goal in the blockchain network: validating transactions and securing the network. Staking, however, involves a different approach. In crypto staking, participants lock up a certain amount of their coins to support the operations of a blockchain network. This process, comparable to a security deposit, is less resource-intensive than mining and offers rewards in the form of transaction fees and additional coins. Now let's talk more about everything and understand the concepts better.
Blockchain vs Mining: The Foundation of Crypto
The blockchain is the bedrock for mining and staking in the cryptocurrency world. It's a decentralized ledger system that securely records transactions across multiple computers.
The role of mining vs. blockchain is fundamental. Miners solve complex mathematical problems to add new blocks to the blockchain. This process requires significant computational power and energy resources, but rewards miners with newly minted cryptocurrency coins.
In contrast, blockchain's role in staking is different. Stakers lock up a certain amount of their coins in a wallet to support the operations of a blockchain network, much like a security deposit. This process is less resource-intensive than mining and offers rewards in the form of transaction fees and additional coins.
Mining vs Staking: Understanding the Pros and Cons
The conventional way of creating new cryptocurrency coins, crypto stake mining, has evolved into a robust industry. Over time, specialized equipment and expansive data centers have become familiar sights in mining operations. Despite its potential for high rewards, mining has significant drawbacks, primarily its environmental impact due to increased energy consumption and the substantial initial investment required for mining hardware.
Crypto staking, a less energy-intensive alternative to mining, has gained popularity among cryptocurrency enthusiasts. Despite the advantages of staking, such as lower resource requirements and reduced barriers to entry, it has its own set of drawbacks. The coins used for staking are typically locked for a period, affecting their liquidity. Furthermore, staking is only supported by some cryptocurrencies, limiting its adoption.
Crypto Mining Benefits
Crypto Mining, a term synonymous with the birth of cryptocurrencies, has been the conventional method of creating new cryptocurrency coins. Over the years, it has grown into a substantial industry, with sophisticated machinery and vast data centers dedicated to mining operations.
Overall, the benefits of crypto mining include the potential for high financial rewards, a tangible way to acquire cryptocurrencies, and enhanced network security through the decentralized validation of transactions. These advantages have attracted many individuals and organizations to engage in mining activities, contributing to the growth and development of the crypto ecosystem.
High Rewards
Crypto mining offers the potential for increased financial rewards. Miners who successfully validate blocks and add them to the blockchain are rewarded with newly minted cryptocurrency coins. This reward system incentivizes miners to dedicate their computational power and resources to the mining process. In the early days of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, when the mining difficulty was relatively low, individuals could mine coins with basic hardware instead and earn significant returns.
Even though the mining landscape has become more competitive over time, with the introduction of specialized mining hardware and large-scale mining operations. There are still opportunities for profitable mining, especially for those who can access low-cost electricity and efficient mining equipment.
Gateway to the Crypto World
For many individuals interested in cryptocurrencies, mining is a practical and tangible way to acquire digital assets. Instead of purchasing coins through exchanges or participating in initial coin offerings (ICOs), mining allows enthusiasts to contribute to the crypto ecosystem and earn coins directly actively. This hands-on approach can provide a deeper understanding of blockchain technology, decentralized networks, and the underlying principles of cryptocurrencies. Mining can be an exciting and educational experience, particularly for newcomers who want to immerse themselves in digital currencies.
Enhanced Network Security
Mining plays a crucial role in maintaining the security and integrity of blockchain networks. In decentralized cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum Classic, miners are responsible for verifying and adding transactions to the blockchain. To achieve this, miners must solve complex cryptographic puzzles, a process known as proof-of-work (PoW). By dedicating computational power and solving these puzzles, miners contribute to the network's overall security. The difficulty of the puzzles ensures that malicious actors cannot easily manipulate or compromise the blockchain. This aspect of mining makes cryptocurrencies resistant to attacks and ensures the immutability of the transaction history, instilling trust and confidence in users.
Crypto Mining Drawbacks
Despite these benefits, mining's weaknesses are hard to ignore. The most significant drawback is its environmental impact due to high-energy consumption. These drawbacks highlight the need for ongoing innovation and exploration of alternative consensus mechanisms that address the environmental impact, reduce the barrier to entry for individual miners, and maintain a fair and secure network.
Environmental Impact
One of the significant drawbacks of crypto mining is its substantial ecological impact. The computational power required for mining, particularly in proof-of-work (PoW) cryptocurrencies, consumes vast electricity. This high energy consumption leads to a significant carbon footprint, contributing to environmental concerns such as increased greenhouse gas emissions and energy wastage. The electricity consumption of mining operations has drawn criticism for its unsustainable nature and the strain it puts on local power grids. As cryptocurrencies gain popularity, there is a growing need for more sustainable mining practices, such as transitioning to renewable energy sources or exploring alternative consensus mechanisms that are more energy-efficient.
High Initial Investment
Another drawback of crypto mining is the substantial upfront investment required, especially for high-end equipment. To mine cryptocurrencies effectively, miners often need specialized hardware, such as ASIC (Application-Specific Integrated Circuit) miners, designed specifically for mining purposes. These mining rigs can be expensive to purchase, maintain, and upgrade as technology advances. Additionally, miners must consider the costs associated with cooling systems, electricity infrastructure, and ongoing operational expenses. The high capital requirements can deter individual miners, leaving mining primarily in the hands of larger-scale operations or mining pools, potentially limiting decentralization in the network.
Increased Mining Difficulty
As more miners participate in the network, the mining difficulty rises to maintain the average block time and ensure a steady issuance of new coins. The increased competition and difficulty mean individual miners have a lower probability of successfully mining a block and earning the associated rewards. This can lead to decreased profitability for miners, making it challenging to recoup their initial investment and operational costs. Additionally, the increased mining difficulty can lead to a higher concentration of mining power among more extensive mining operations that can afford more powerful equipment, potentially raising concerns about centralization and network security.
Crypto Staking Benefits
As an alternative to the energy-intensive mining process, crypto staking has emerged as a popular choice among cryptocurrency enthusiasts. Staking presents a different approach to achieving consensus and validating transactions on the blockchain.
Lower resource requirement
One of the significant benefits of crypto staking is its lower resource requirement compared to traditional mining. In the mining process, powerful hardware and substantial computational power are necessary to solve complex mathematical puzzles and validate transactions on the blockchain. This high-energy consumption has raised concerns about its environmental impact, mainly due to the carbon footprint associated with mining operations. In contrast, staking relies on a Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism, where participants are chosen to validate transactions based on the number of coins they hold and "stake" in the network. This approach eliminates energy-intensive calculations, resulting in a more energy-efficient and environmentally friendly alternative.
Reduced barrier to entry
Staking provides a more accessible entry point for individuals who want to participate in the cryptocurrency ecosystem. Participants can stake their cryptocurrency holdings and contribute to the network's security and consensus process. Traditional mining often requires significant upfront investments in specialized hardware, such as ASIC (Application-Specific Integrated Circuit) miners, and high electricity costs. In contrast, staking typically requires a smaller amount of initial capital. This reduced barrier to entry enables a broader range of individuals to get involved in blockchain networks and benefit from the rewards and incentives offered through staking.
Chance to earn rewards
Staking allows participants to earn rewards for contributing to the network. When users stake their coins, they actively participate in the consensus process and help validate transactions. As a reward for their involvement, participants receive additional cryptocurrency tokens. The reward system varies depending on the specific blockchain network and its staking protocol. In some cases, the rewards can be proportional to the number of coins staked, incentivizing participants to hold and contribute to the network's security and stability. This mechanism promotes network participation and allows individuals to generate passive income from their cryptocurrency holdings.
Crypto Staking Drawbacks
Despite these advantages, staking has its drawbacks. When you stake mining, they are locked for a period, restricting their liquidity. This aspect means that any decrease in the cryptocurrency's market value during the lock-in period could affect your investment negatively.
Despite these drawbacks, crypto staking continues to be an attractive option for many cryptocurrency enthusiasts. It offers benefits such as lower resource requirements, reduced barriers to entry, and the opportunity to earn rewards. However, individuals considering staking should carefully evaluate the liquidity restrictions and the availability of staking options for their chosen cryptocurrencies, taking into account their investment goals and risk tolerance.
Liquidity restriction
One significant drawback of crypto staking is the liquidity restriction imposed on staked coins. When participants stake their cryptocurrency, they typically commit to locking up their coins for a specific period. During this time, the staked coins could not be freely traded or accessed. The lock-up period can vary depending on the blockchain network and staking protocol, ranging from a few days to several months or even years. This lack of liquidity can be a disadvantage for individuals who may require immediate access to their funds or want to take advantage of trading opportunities in the market. Furthermore, if the market value of the staked cryptocurrency decreases during the lock-up period, participants may experience losses in terms of the value of their investment.
Limited adoption
While crypto staking has gained popularity, it is important to note that not all cryptocurrencies support this method. Some cryptocurrencies, such as Bitcoin, continue to rely on the proof-of-work (mining) consensus mechanism. Staking is more commonly associated with cryptocurrencies that implement the proof-of-stake (PoS) or delegated proof-of-stake (DPoS) consensus algorithms. Although the number of cryptocurrencies adopting staking is growing, the limited availability of staking options can restrict the choices of individuals who wish to participate in staking activities. However, it is worth mentioning that there is an ongoing trend in the industry toward transitioning from mining to staking, as seen with Ethereum's shift to Ethereum 2.0. This indicates a gradual shift in the consensus mechanisms used by cryptocurrencies, potentially increasing the opportunities for staking in the future.
Staking vc Mining: A Comparative Analysis
When choosing between staking and mining, the decision often hinges on individual circumstances and preferences. Both methods have unique benefits and potential drawbacks, highlighting the importance of careful consideration.
Considering the profitability aspect, the choice between mining and staking becomes complex. Mining is highly profitable, particularly for those with access to cheap electricity and substantial initial investment for acquiring the necessary hardware. On the other hand, staking offers the advantage of predictable returns and lower operating costs.
One cannot ignore the environmental impacts of both mining and staking. While it's evident that mining consumes a significant amount of energy, it's crucial to note that staking also has energy requirements. While they are considerably less than mining, staking necessitates the coins to be kept in 'always-online' wallets, contributing to energy consumption.
In terms of security, both mining and staking contribute significantly to the blockchain network's resilience. Mining secures the network through the computational work of miners, whereas staking ensures network security by incentivizing stakes to act honestly. Under the staking mechanism, any malicious activity could result in the loss of staked coins, ensuring network integrity.
| Aspects | Mining | Staking |
|---|---|---|
| Profitability | Highly profitable with significant initial investment and access to cheap electricity | Predictable returns, lower operating costs |
| Environmental Impact | Consumes a significant amount of energy | Requires energy for 'always-online' wallets |
| Security | Secures the network through computational work | Incentivizes stakes to act honestly, loss of staked coins for malicious activity |
| Considerations | Requires expensive hardware and ongoing maintenance | Coins need to be kept in 'always-online' wallets |
| Flexibility | Can mine various cryptocurrencies | Usually limited to staking specific cryptocurrencies |
Where to get data to monitor the cryptocurrency market?
Coin Price List is a highly beneficial platform for crypto investors and enthusiasts, offering a comprehensive suite of features for accessing and analyzing crypto pair data and monitoring cryptocurrency market data. As a real-time, flexible, and reliable solution, it presents significant advantages for startups seeking swift growth in the ever-changing crypto market.
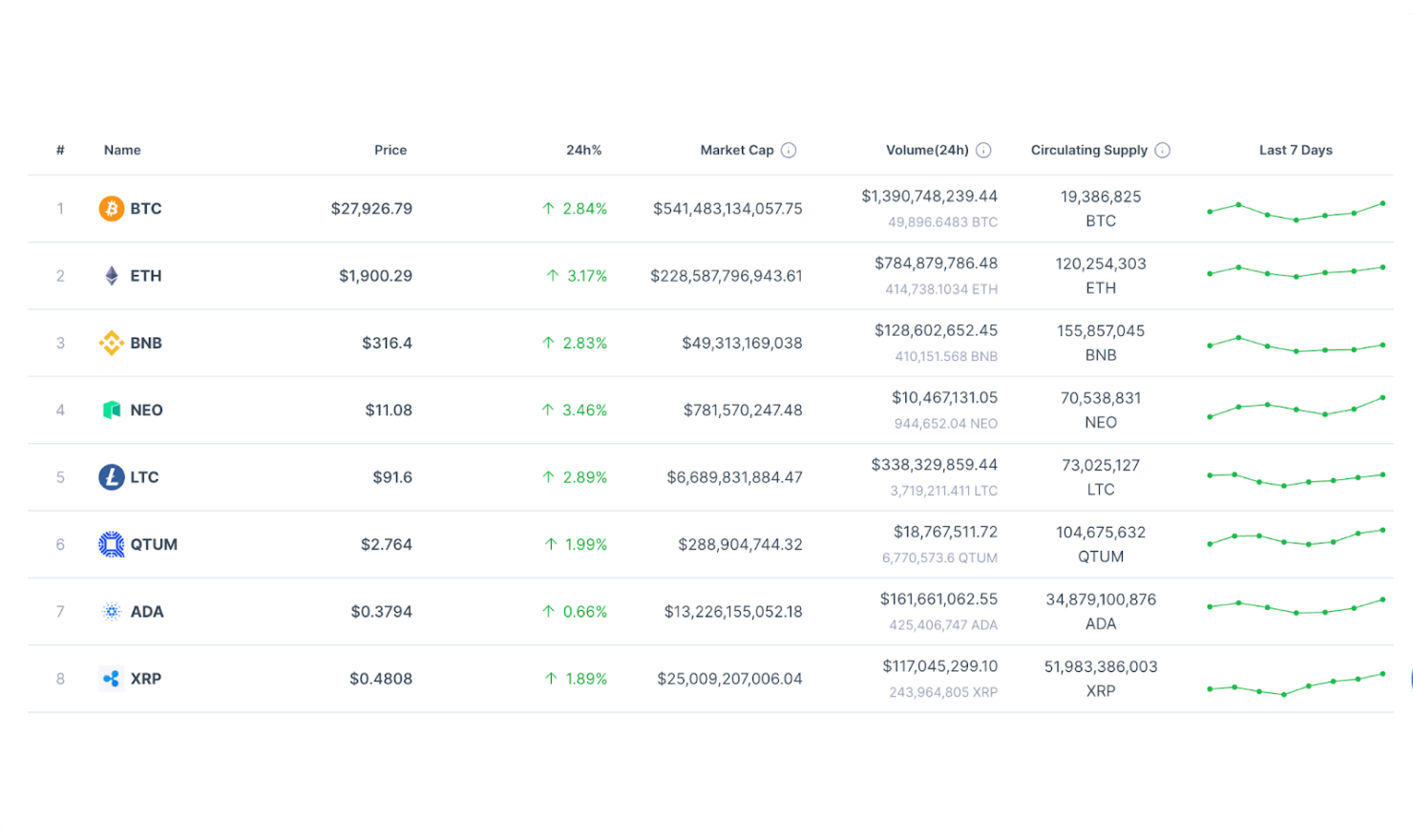
The platform's startup-friendly nature is a boon for fast-paced businesses. With scalable solutions, companies can quickly adapt their data access needs as they expand. This flexibility, combined with the prompt and reliable services offered by Coin Price List, ensures that startups can swiftly test hypotheses and launch minimum viable products (MVPs).
Coin Price List stands for open rates and a fair data market, offering a range of pricing plans to suit varying business needs. Companies only pay for their services, making it an economical solution. As the business grows, it can easily switch to a plan with higher capacities.
Born as an in-house solution, Coin Price List was developed with precise mathematical logic and an emphasis on ease of implementation. The platform's dev-to-dev approach underscores its efficiency and reliability. With detailed step-by-step documentation and resources, businesses can swiftly integrate Coin Price List into their projects, freeing up their focus for other tasks.
Coin Price List is all about staying updated. The platform continually evolves to provide the most accurate, up-to-date, and timely crypto market data, regularly updating its service for an enhanced user experience. Every update brings new features to your project, driving Coin Price List's commitment to innovation and growth.
In terms of operation, Coin Price List gathers raw data from various sources, crafting detailed information about the cryptocurrency market. Cryptocurrency prices on the main page are updated in real-time with each page reload. This real-time updating extends to the public API, ensuring users always have the most current data. This real-time, reliable access to data makes Coin Price List an invaluable tool for crypto investors and enthusiasts.
Final Thoughts on Staking vs. Mining: Making the Right Choice
The mining vs staking debate remains at the forefront as the crypto landscape evolves. The right choice often depends on resource availability, risk tolerance, investment horizon, and personal preferences.
For some, the traditional mining process might seem appealing due to its potential for high rewards. Meanwhile, others may prefer staking for its lower resource requirements and environmental friendliness. It's also worth considering that staking offers a more predictable income stream, whereas mining rewards can be sporadic and uncertain. Regardless of the choice, it's crucial to understand the workings, benefits, and potential risks associated with each method. As we look toward the future, it's evident that both mining and staking will continue to play significant roles in the ever-evolving blockchain ecosystem.
Remember, whether you choose to mine or stake, you're not only earning rewards but also contributing to the security and efficiency of the blockchain network. So, choose wisely, and may your crypto journey be rewarding!
Recent posts

How Can Dune Analytics Highlight Shilling Activity?
Uncover 'shilling' in crypto using Dune Analytics. Understand how Dune helps users tackle shilling. Stay one step ahead with reliable data Coin Price List.
12/07/2023

What Is Shilling? What is Shilling's impact on the Crypto Market?
Crypto shilling can reshape the dynamics of the digital currency world. Learn about this fascinating phenomenon and its potential implications for crypto traders.
21/06/2023